1. 스레드
- 다중 스레딩 : 하나의 프로그램이 동시에 여러 가지 작업을 할 수 있도록 하는 것
- 스레드 : 각각의 작업, 동일한 데이터를 공유함
- 프로세스 : 자신만의 데이터를 가짐
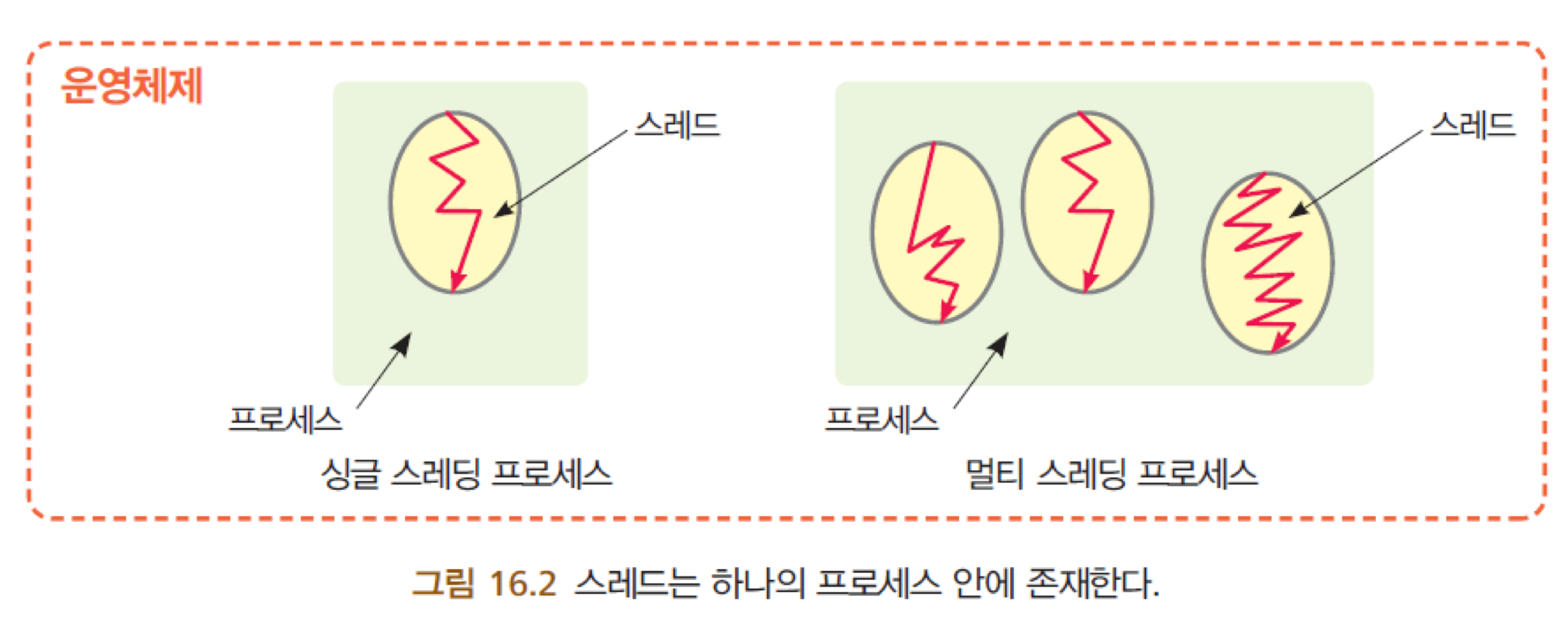
- 프로그램을 보다 빠르게 실행하기 위해 멀티 스레딩 사용
2. 멀티 스레딩의 문제점
- 여러 스레드들이 같은 데이터를 공유하게 되면 '동기화' 문제 발생
3. 스레드 생성과 실행
Thread t = new Thread();
t.start();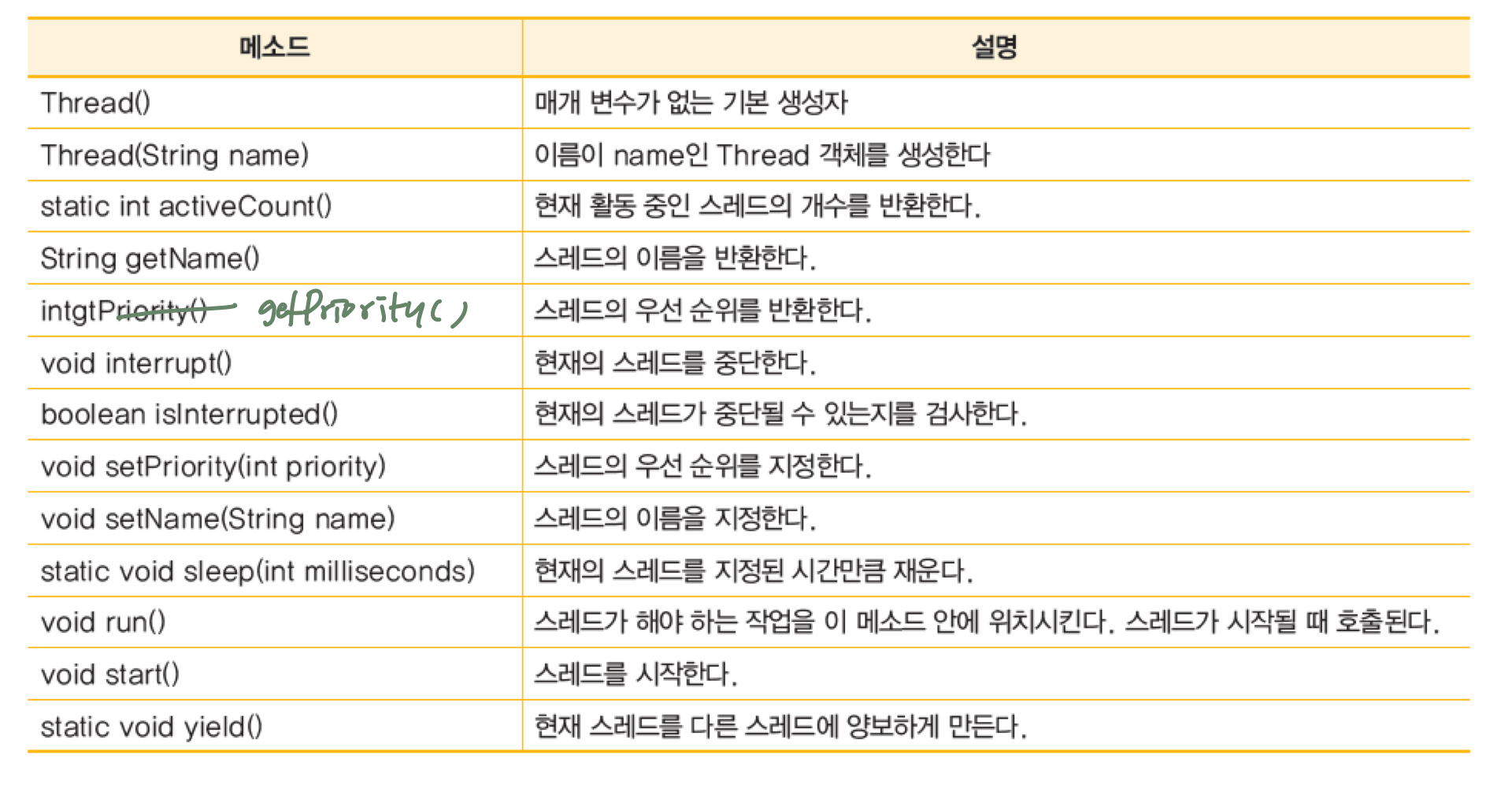
3-1) 스레드 생성: Thread 클래스 상속하는 방법
- Thread 클래스를 상속받은 후에 run() 메소드 재정의
- run 메소드 안에 작업 기술
- Thread 객체 생성하고 start() 호출해서 스레드 시작
class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
public class MyThreadTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Thread t = new MyThread();
t.start();
}
}
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
3-2) 스레드 생성: Runnable 인터페이스 구현하는 방법
- Runnable 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스 작성
- run() 메소드 작성
- Thread 객체 생성하고 Runnable 객체 인수로 전달
- start() 호출해서 스레드 시작
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
public class MyRunnableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new MyRunnable());
t.start();
}
}
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
- 스레드 2개 예제
class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i ++) {
System.out.print("[" + i + "]");
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main start");
MyThread mt = new MyThread();
mt.start();
MyThread mt2 = new MyThread();
mt2.start();
Thread t = new Thread(new MyRunnable()); // runnable -바로 스타트 불가.
t.start();
// 모든 작업이 끝났을 때 종료 메세지를 출력하고 싶은 경우
mt.join();
mt2.join();
t.join(); // 끝날 때까지 기다리기
System.out.println("\nmain end");
}
}
/**
main start
0 1 2 3 4 0 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 [0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29]
main end
**/
- 람다식 이용한 스레드 작성
public class LambdaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable task = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
System.out.print(i + " ");
};
new Thread(task).start();
}
}
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
4. 스레드 상태
- New : Thread 클래스의 인스턴스는 생성되었지만, start() 메소드를 호출하기 전
- Runnable : start() 메소드가 호출되어 실행 가능한 상태, 하지만 아직 스케줄러가 선택하지 않았으므로 실행 상태는 아님
- Running : 스레드 스케줄러가 스레드를 선택하면, 실행 중인 상태가 됨
- Blocking : 스레드가 아직 살아있지만, 여러 이유로 현재 실행할 수 없는 상태
- Terminated : 스레드가 종료된 상태, run() 메소드가 종료되면 스레드도 종료됨
- 실행 가능 상태 : 스레드가 스케줄링 큐에 넣어지고, 스케줄러에 의해 우선순위에 따라 실행
- 실행 중지 상태
- 스레드나 다른 스레드가 suspend()를 호출하는 경우
- 스레드가 wait() 호출하는 경우
- 스레드가 sleep() 호출하는 경우
- 스레드가 입출력 작업을 하기 위해 대기하는 경우
5. 스레드 스케줄링
- 대부분 스레드 스케줄러는 선점형 스케줄링과 타임 슬라이싱을 사용해 스레드 스케줄링
- 어떤 스케줄링을 선택하느냐는 JVM에 의해 결정됨
6. 스레드 우선순위
- 1 ~ 10 사이의 숫자료 표시됨
- 기본 우선순위 : NORM_PRIORITY(5)
- MIN_PRIORITY(1)
- MAX_PRIORITY(10)
- void setPriority(int newPriority) : 현재 스레드의 우선 순위 변경
- getPriority() : 현재 스레드의 우선 순위 반환
7. sleep()
- 지정된 시간동안 스레드 재움
- 스레드가 수면 상태로 있는 동안 인터럽트되면 InterruptedException 발생
- 4초 간격으로 메시지 출력
public class SleepTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
String messages[] = {"Hello.",
"My name is A.",
"I'm majoring in computer science.",
"I'm taking a JAVA class."};
for (int i = 0; i < messages.length; i++) {
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println(messages[i]);
}
}
}
/**
Hello.
My name is A.
I'm majoring in computer science.
I'm taking a JAVA class.
**/
8. join()
- 스레드가 종료될 때까지 기다리는 메소드
- 특정 스레드가 작업을 완료할 때까지 현재 스레드의 실행을 중지하고 기다리는 것
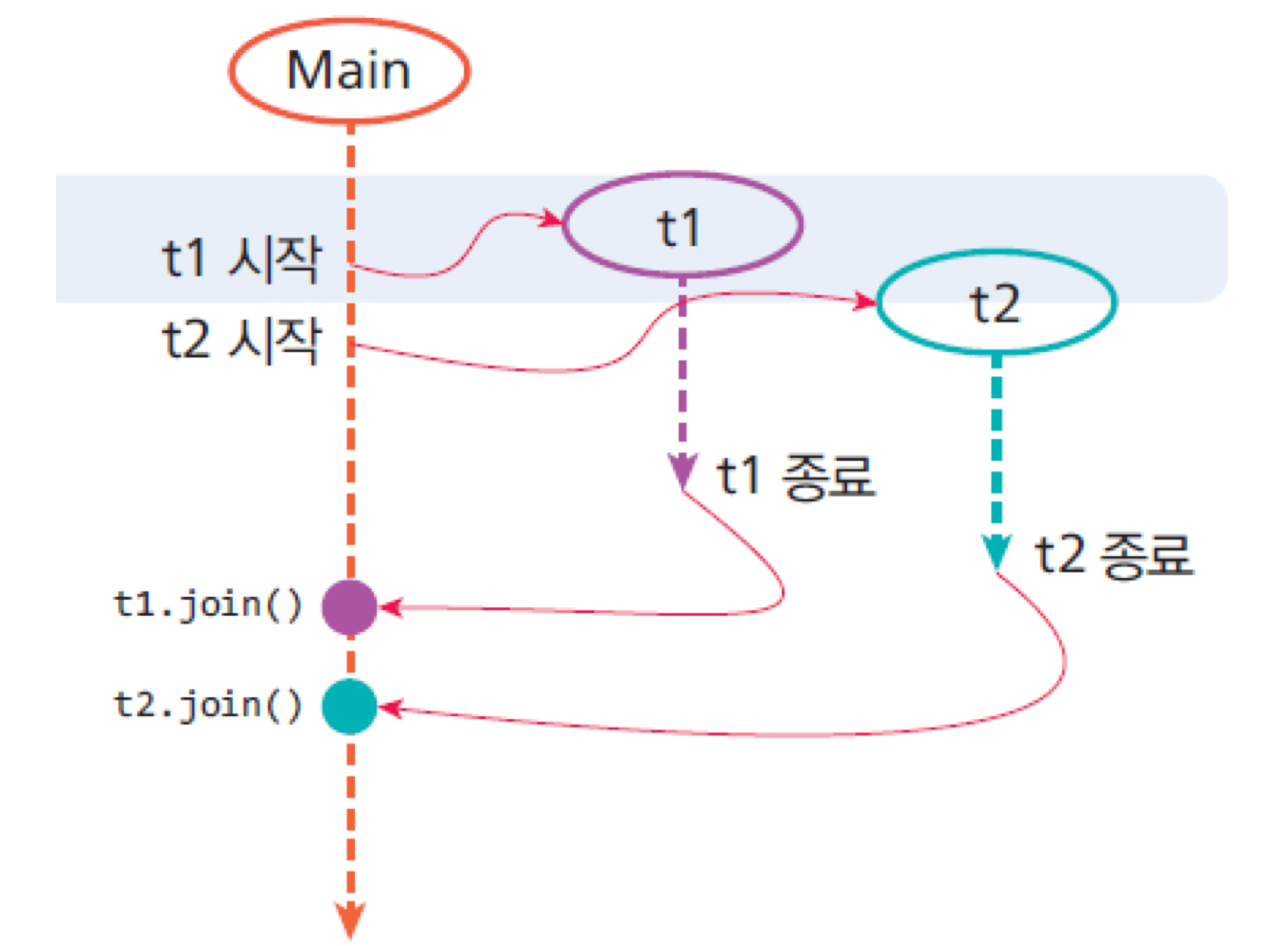
9. 인터럽트와 yield()
- 인터럽트 : 하나의 스레드가 실행하고 있는 작업을 중지하도록 하는 메커니즘 -> 대기 상태나 수면 상태가 됨
- yield() : CPU를 다른 스레드에게 양보하는 메소드
10. 자바 스레드 풀
- 스레드 풀 : 미리 초기화된 스레드들이 모여 있는 곳
- 스레드 풀의 동일한 스레드를 사용하여 N개의 작업을 쉽게 실행할 수 있음
- 스레드의 개수보다 작업의 개수가 더 많은 경우, 작업은 FIFO 큐에서 기다려야 함
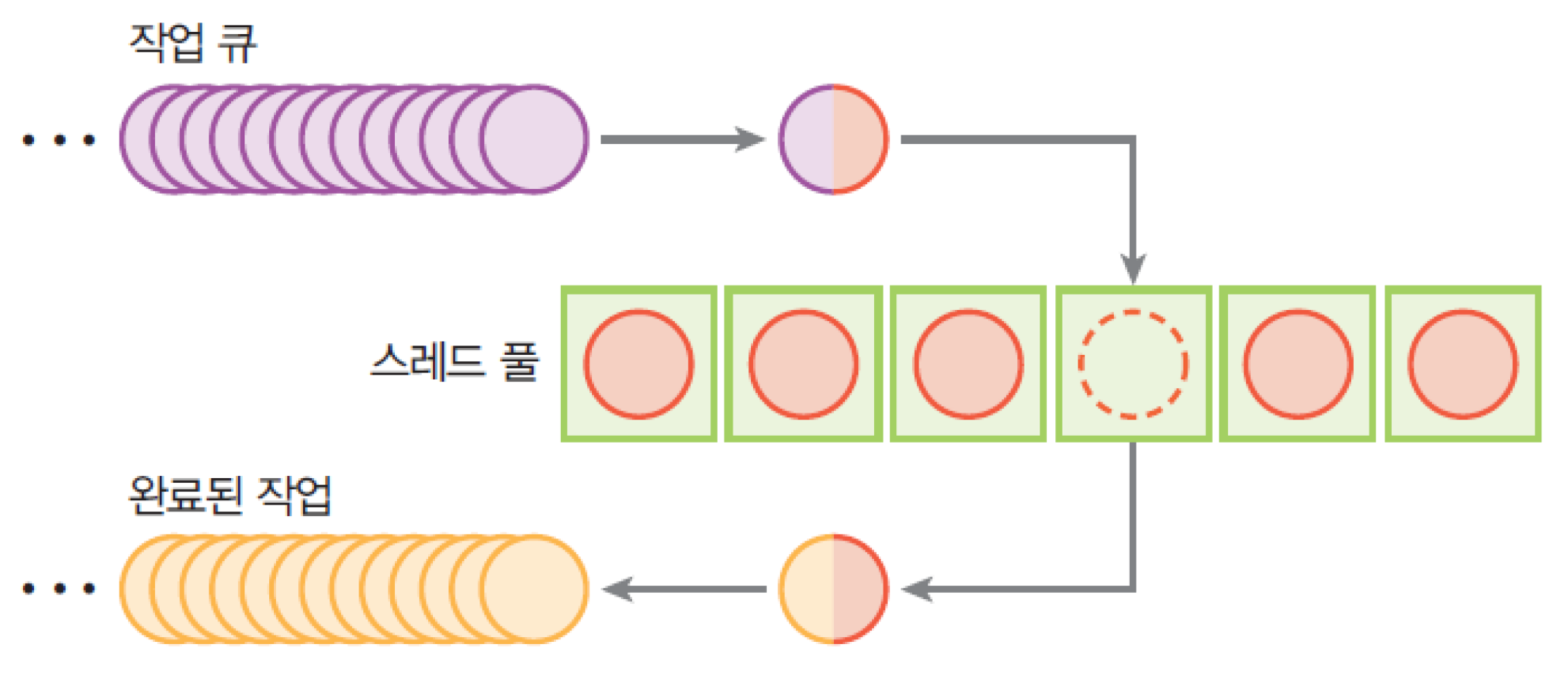
- Java5 부터 자바 API는 Executor 프레임워크 제공
-> 개발자는 Runnable 객체를 구현하고 ThreadPoolExecutor로 보내기만 하면 됨
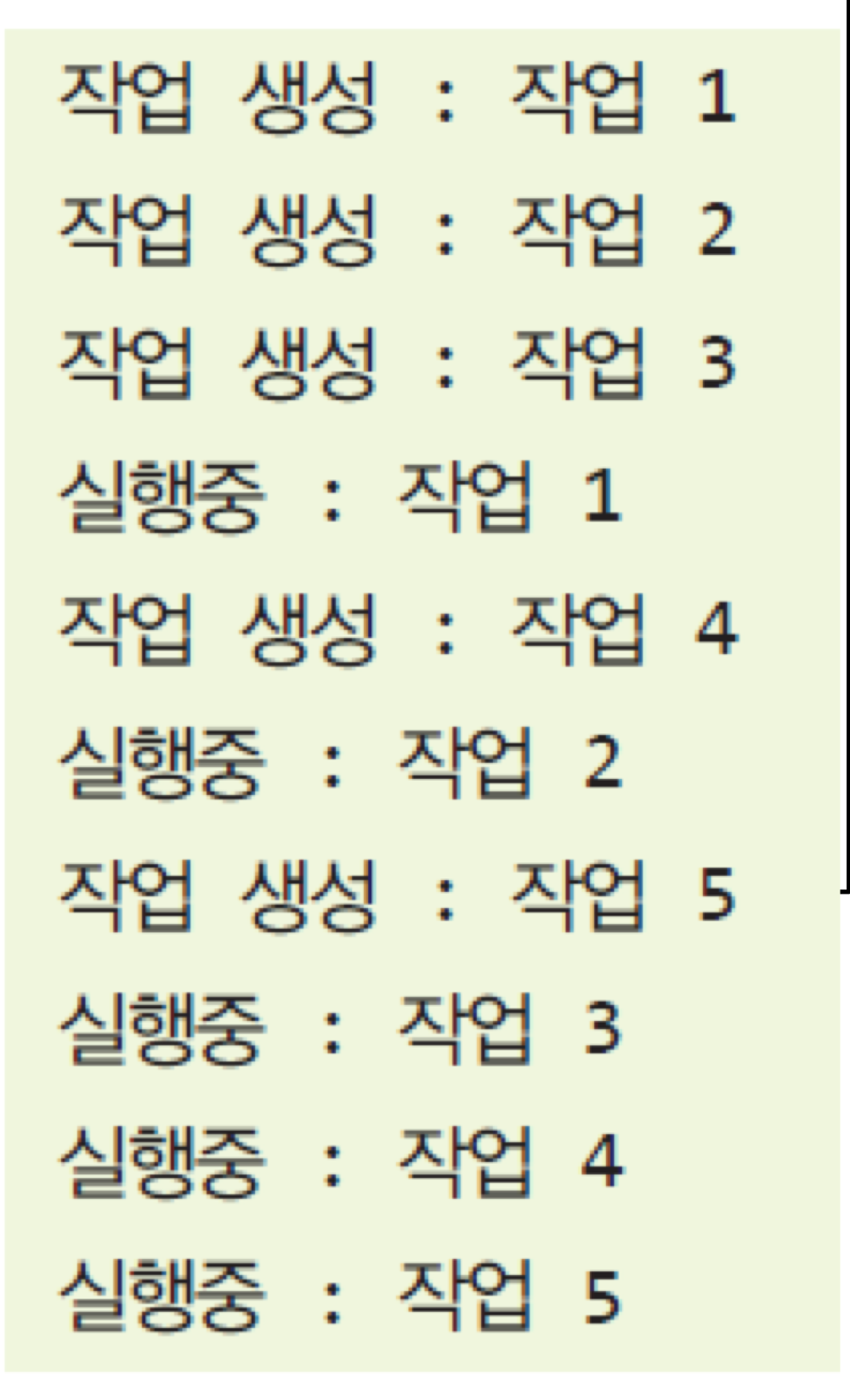
class MyTask implements Runnable {
private String name;
public MyTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("실행중 : " + name);
Thread.sleep(long)(Math.random() * 1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = (ThreadPoolExecutor) Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
for(int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
MyTask task = new MyTask("작업 " + i);
System.out.println("작업 생성 : " + task.getName());
executor.execute(task);
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}
11. 스레드 사용시 주의해야 할 점
- 동일한 데이터를 공유하기 때문에 매우 효율적으로 작업할 수 있지만, 2가지의 문제가 발생할 수 있음
- 문제 예제
class Printer {
void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
}
class MyThread1 extends Thread {
Printer prn;
int[] myarr = {10, 20, 30, 40};
MyThread1(Printer prn) { this.prn = prn; }
public void run() { prn.print(myarr); }
}
class MyThread2 extends Thread {
Printer prn;
int[] myarr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
MyThread2(Printer prn) { this.prn = prn; }
public void run() { prn.print(myarr); }
}
public class TestSynchro {
pubilc static void main(String args[]) {
Printer obj = new Printer();
MyThread1 t1 = new MyThread1(obj);
MyThread2 t2 = new MyThread2(obj);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
// 1 10 20 2 30 3 4 40
// 순서는 계속 바뀔 수 있음, 둘이 섞여서 엉망으로 출력됨
11-1) 동기화 (Synchronization)
- 한 번에 하나의 스레드만이 공유 데이터를 접근할 수 있도록 제어하는 것이 필요
- 자원에 한 번에 하나의 스레드만이 접근할 수 있고, 하나의 스레드 작업이 끝나면 다음 스레드가 사용할 수 있도록 하여 해결
- 자바에서의 동기화 방법
- 동기화 메소드
- 동기화 블록
- 정적 동기화
- 락(lock) 또는 모니터(monitor) 사용
// 메소드 앞에 synchronized 키워드 붙이기
class Printer {
synchronized void print(int[] arr) {
....
}
}
// 10 20 30 40 1 2 3 4
// 부분 코드만 동기화 -> synchronized 블록으로 설정
class Printer {
void print(int[] arr) throws Exception {
synchronized(this) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
}
}
12. 교착 상태, 기아 상태
- 동일한 자원을 접근하려고 동기화를 기다리면서 대기하는 스레드들이 많아지면 JVM이 느려지거나 일시 중단 되기도 함
- 문제 예제
public class DeadLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final String res1 = "Gold";
final String res2 = "Silver";
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized(res1) {
System.out.println("Thread 1 : 자원 1 획득");
try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (Exception e) {}
synchronized(res2) {
systme.out.println("Thread 1 : 자원 2 획득");
}
}});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized(res2) {
System.out.println("Thread 2 : 자원 2 획득");
try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (Exception e) {}
synchronized(res1) {
System.out.println("Thread 2 : 자원 1 획득");
}
}});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
// Thread 1 : 자원 1 획득
// Thread 2 : 자원 2 획득
12-1) 방법1 : 잠금 순서 변경
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized(res1) {
System.out.println("Thread 2 : 자원 1 획득");
try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (Exception e) {}
synchronized(res2) {
System.out.println("Thread 2 : 자원 2 획득");
}
}});
/**
Thread 1 : 자원 1 획득
Thread 1 : 자원 2 획득
Thread 2 : 자원 1 획득
Thread 2 : 자원 2 획득
**/
12-2) 방법2: 스레드 간의 조정
13. wait(), notify()
- 이벤트가 발생하면 알리는 방법
- 생산자/소비자 문제에 적용
// buffer 클래스
class Buffer {
private int data;
private boolean empty = true;
public synchronized int get() {
while (empty) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
empty = true;
notifyAll();
return data;
}
public synchronized void put(int data) {
while (!empty) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
empty = false;
this.data = data;
notifyAll();
}
}
// 생산자
class Producer implements Runnable {
private Buffer buffer;
public Producer(Buffer buffer) {
this.buffer = buffer;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
buffer.put(i);
System.out.println("생산자: " + i + "번 케익을 생산하였습니다.");
try {
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
// 소비자
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private Buffer buffer;
public Consumer(Buffer drop) {
this.buffer = drop;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int data = buffer.get();
System.out.println("소비자: " + data + "번 케익을 소비하였습니다.");
try {
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
public class ProducerConsumerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Buffer buffer = new Buffer();
(new Thread(new Producer(buffer))).start();
(new Thread(new Consumer(buffer))).start();
}
}
/**
생산자: 0번 케익을 생산하였습니다.
소비자: 0번 케익을 소비하였습니다.
생산자: 1번 케익을 생산하였습니다.
소비자: 1번 케익을 소비하였습니다.
...
생산자: 9번 케익을 생산하였습니다.
소비자: 9번 케익을 소비하였습니다.
**/'Software > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Baekjoon] 1085.직사각형에서 탈출 (0) | 2023.04.03 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] Day13. 파일 입출력 (0) | 2023.01.18 |
| [JAVA] Day12. 제네릭과 컬렉션 (0) | 2023.01.11 |
| [JAVA] Day11. 자바 그래픽 (5) | 2023.01.10 |
| [JAVA] Day10. 스윙 컴포넌트 (0) | 2023.01.09 |