C언어와 비슷한 문법!
1. if-else문
public class Nested {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 입력: ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
if (num > 0)
System.out.println("양수");
else if (num == 0)
System.out.println("0");
else
System.out.println("음수");
}
}
2. switch문
- 제어식에 숫자, 문자, 문자열 가능
import java.util.*;
public class Score2Grade {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score, num;
char grade;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("성적 입력: ");
score = sc.nextInt();
num = score / 10;
switch(num) {
case 10:
case 9: grade = 'A'; break;
case 8: grade = 'B'; break;
case 7: grade = 'C'; break;
case 6: grade = 'D'; break;
default: grade = 'F'; break;
}
System.out.println("학점: " + grade);
}
}switch(num) {
case 10:
case 9: return 'a';
case 10, 9 -> return 'a';
}
// 둘 다 가능
3. for문
- for (초기식; 조건식; 증감식) {
}
public class Sum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("1부터 10까지의 정수의 합 = %d" + sum)l
}
}
4. while문
- while (조건식) {
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GetSum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = 0, value = 0;
while (value != -1) {
sum += value;
System.out.print("정수 입력: ");
value = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("정수의 합은 " + sum + "입니다.");
}
}
5. do-while문
- 조건이 참인 동안 do 안의 문장 반복
- 우선 do 문장 한 번 실행하고 조건 확인
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CheckInput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int month;
do {
System.out.print("올바른 월을 입력하세요 [1-12]: ");
month = sc.nextInt();
} while (month < 1 || month > 12);
System.out.println("사용자가 입력한 월은 " + month);
}
}
6. break, continue
- break: 반복문을 벗어남
- continue: 해당 반복을 멈추고 다음 반복으로 넘어감
7. 무한루프
- while문에서 종료 조건을 만들기 까다로운 경우 while(true)를 이용한 후 그 안에서 break문으로 반복을 빠져나가는 것이 좋음
8. 배열 선언과 사용
- 자바에서 배열은 객체
// 배열 생성
int[] s = new int[10];
// 배열 채우기
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
s[i] = i;
}
// 배열 출력
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
System.out.print(s[i] + " ");
}
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9- 배열의 크기: s.length
// 배열 초기화
int [] scores = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
9. for-each 루프
int[] list = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int e : list) {
System.out.println(e);
}
// 배열 전부 출력
10. 2차원 배열
// 2차원 배열 생성
int[][] s = new int[3][5];
// 2차원 배열 초기화
int[][] testArray = {
{10, 20, 30, 1, 2},
{40, 50, 60, 3, 4},
{70, 80, 90, 5, 6}
};
// 2차원 배열 출력
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.println(s[i][j]);
}
}
11. 래그드 배열
int[][] ragged = new int[MAX_ROWS + 1][];
for (int r = 0; r <= MAX_ROWS; r++)
ragged[r] = new int[r+1];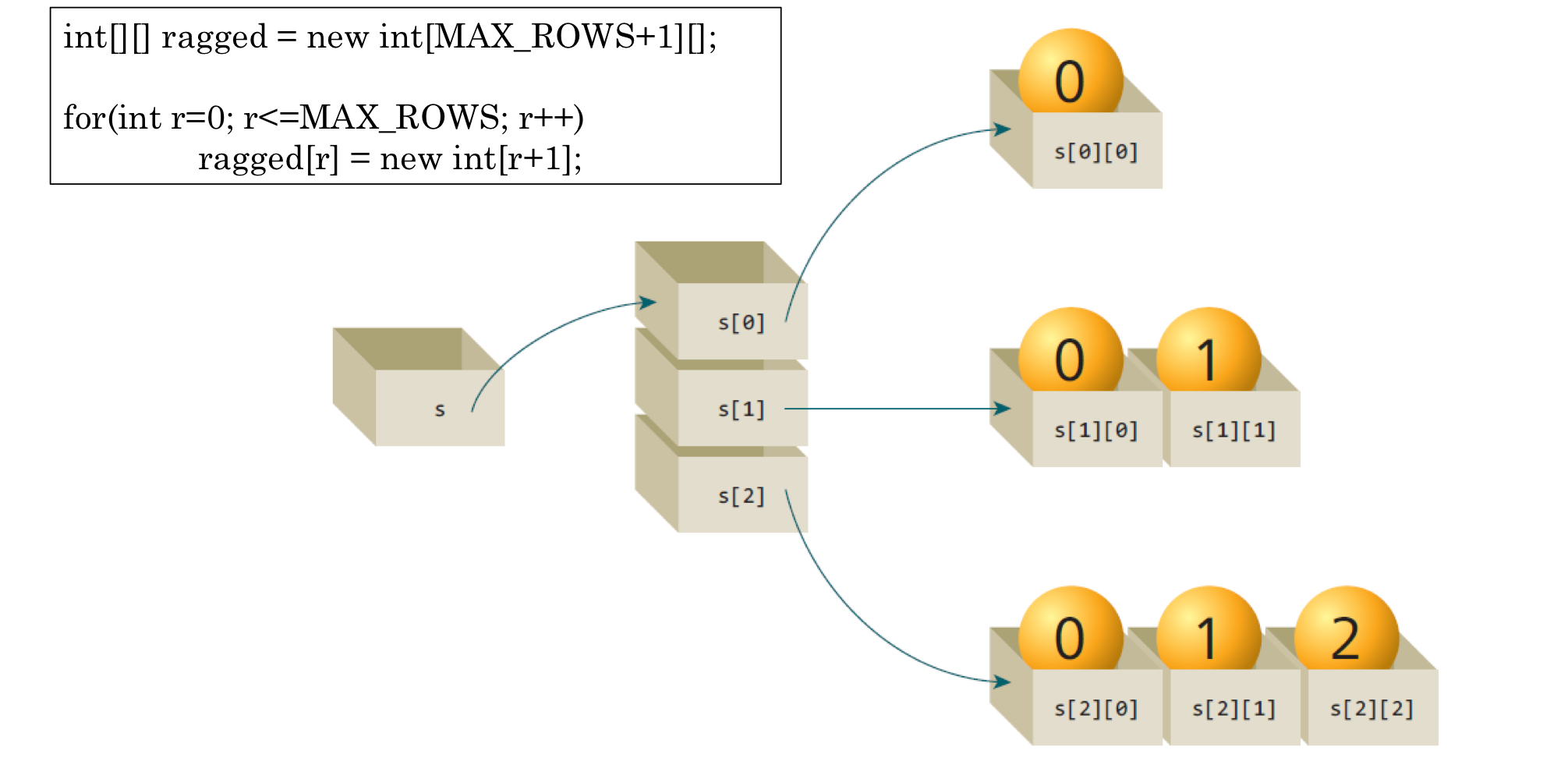
public class RaggedArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] ragged = new int[3][];
ragged[0] = new int[1];
ragged[1] = new int[2];
ragged[2] = new int[3];
for (int r = 0; r < ragged.length; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < ragged[r].length; c++)
ragged[r][c] = c;
}
}
}
12. ArrayList
- 배열의 크기 동적 변경하면서 사용 가능
ArrayList<String> list; // list: 문자열을 저장하는 ArrayList 참조 변수 선언
list = new ArrayList<>(); // ArrayList 생성
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Grape");import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new Arraylist<>();
list.add("Anna");
list.add("Mike");
list.add("Joy");
list.add("Lina");
for (String obj : list)
System.out.print(obj + " ");
}
}
// Anna Mike Joy Lina'Software > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] Day5. 상속 (0) | 2022.12.29 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] Day 3-4. 클래스와 객체 (2) | 2022.12.29 |
| [JAVA] Day1. 자바 기초 (0) | 2022.12.27 |
| [JAVA] 예외처리 (0) | 2021.07.22 |
| [JAVA] 객체지향 (0) | 2021.07.22 |